What Makes Blue: A Comprehensive Guide To The Science Of Color
When we look at the sky or the ocean, we see the color blue, but what exactly makes something blue?
The color blue is caused by the way light interacts with objects. When white light hits an object, some of the light is absorbed and some is reflected. The color of the object depends on which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected. Blue objects absorb red and green light and reflect blue light. This is why we see the sky and the ocean as blue.
The color blue has many important benefits. It can be calming and relaxing, and it has been shown to improve sleep and reduce stress. Blue is also a popular color for clothing and home dcor, and it can be used to create a variety of different moods and atmospheres.
Here are some of the key aspects of what makes blue:
What Makes Blue
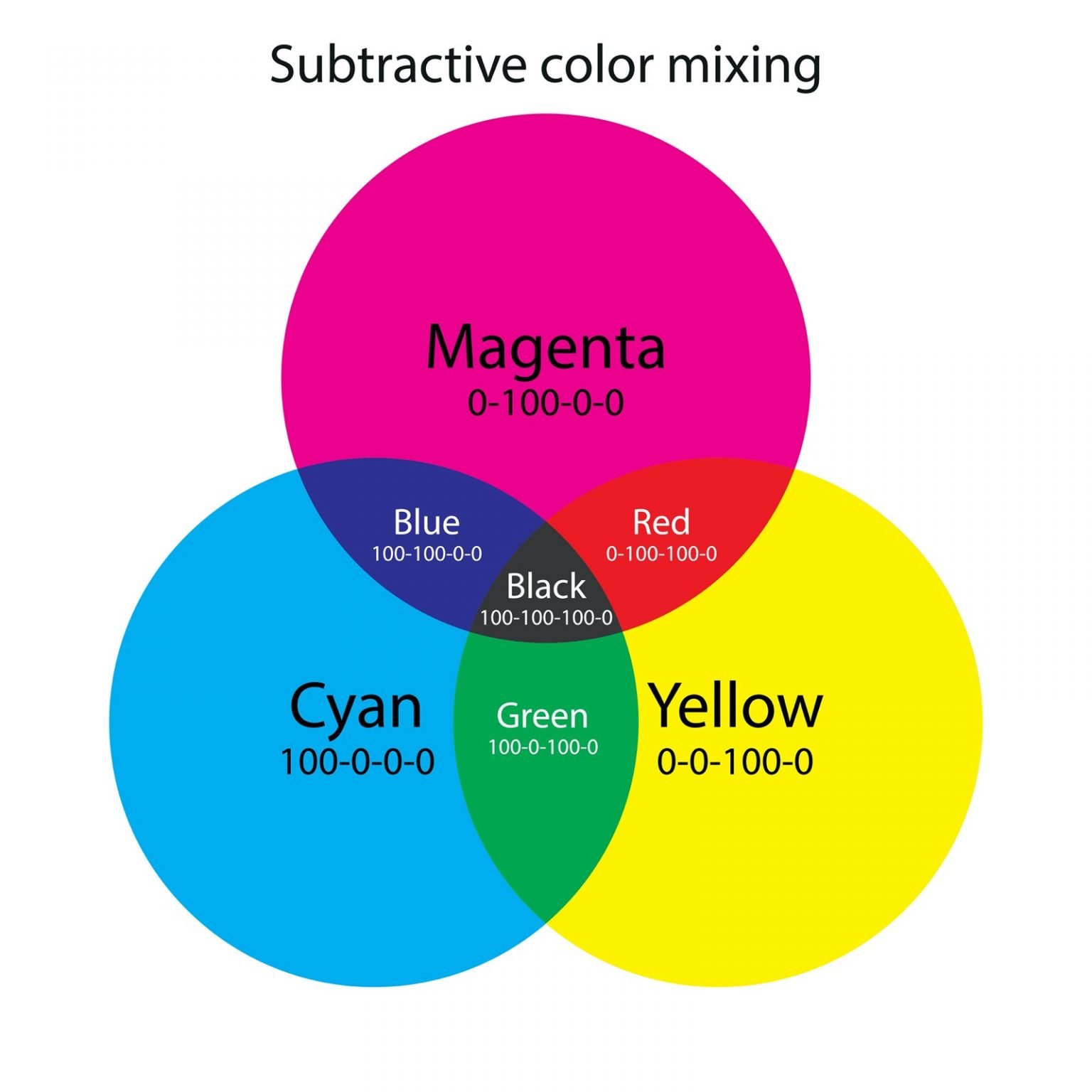
- Light and Wavelength: Blue is a color that is created when light with a wavelength between 450 and 495 nanometers is reflected off an object.
- Absorption and Reflection: When white light hits an object, some of the light is absorbed and some is reflected. The color of the object depends on which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected. Blue objects absorb red and green light and reflect blue light.
- The Sky and the Ocean: The sky and the ocean appear blue because they scatter blue light more than other colors of light. This is because blue light has a shorter wavelength than other colors of light, and shorter wavelengths are scattered more easily.
The Importance of Blue
- Calming and Relaxing: Blue has been shown to have a calming and relaxing effect on the human body. This is why blue is often used in bedrooms and other places where people want to relax.
- Improves Sleep: Blue light has been shown to improve sleep quality. This is because blue light helps to regulate the body's circadian rhythm, which is the natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Reduces Stress: Blue has been shown to reduce stress levels. This is because blue light helps to lower the levels of cortisol, a hormone that is associated with stress.
- Popular Color: Blue is a popular color for clothing and home dcor. This is because blue is a versatile color that can be used to create a variety of different moods and atmospheres.
What Makes Blue
The color blue is all around us, from the sky to the ocean to our clothing. But what exactly makes something blue? The answer lies in the way that light interacts with objects.
- Light and Wavelength: Blue is a color that is created when light with a wavelength between 450 and 495 nanometers is reflected off an object.
- Absorption and Reflection: When white light hits an object, some of the light is absorbed and some is reflected. The color of the object depends on which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected. Blue objects absorb red and green light and reflect blue light.
- The Sky and the Ocean: The sky and the ocean appear blue because they scatter blue light more than other colors of light. This is because blue light has a shorter wavelength than other colors of light, and shorter wavelengths are scattered more easily.
- Blue in Nature: Blue is a common color in nature, found in flowers, birds, and even some animals. Blueberries, for example, get their color from a pigment called anthocyanin.
- Blue in Art and Culture: Blue has been used in art and culture for centuries. In many cultures, blue is associated with the sky, water, and peace.
- Blue in Science and Technology: Blue is also an important color in science and technology. For example, blue lasers are used in a variety of applications, including optical storage and laser surgery.
These are just a few of the key aspects that make blue such a fascinating and versatile color. From its origins in the physics of light to its cultural and scientific significance, blue is a color that has captured the human imagination for centuries.
- Wentworth Miller Wife And Kids
- Shane West Wife
- Who Is Josh Allens Twin Brother
- Nina Aouilk Mother
- Larry Fink Daughter
Light and Wavelength
The connection between light and wavelength and what makes blue is fundamental. The wavelength of light determines the color that we perceive. When white light hits an object, some of the light is absorbed and some is reflected. The color of the object depends on which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected.
In the case of blue objects, they absorb red and green light and reflect blue light. This is why we see the sky and the ocean as blue. The sky scatters blue light more than other colors of light, and the ocean absorbs red and green light and reflects blue light.
The understanding of the connection between light and wavelength and what makes blue is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps us to understand the nature of color and how we perceive it. Second, it has practical applications in a variety of fields, such as art, design, and photography.
For example, artists use their understanding of color to create specific effects in their paintings. Designers use their understanding of color to create visually appealing products and environments. And photographers use their understanding of color to capture beautiful and evocative images.
Overall, the connection between light and wavelength and what makes blue is a fascinating and important topic with a wide range of applications in the real world.
Absorption and Reflection
The connection between absorption and reflection and what makes blue is fundamental. Absorption and reflection are the processes by which light interacts with objects and determines their color. In the case of blue objects, they absorb red and green light and reflect blue light. This is why we see the sky and the ocean as blue.
The understanding of absorption and reflection is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps us to understand the nature of color and how we perceive it. Second, it has practical applications in a variety of fields, such as art, design, and photography.
For example, artists use their understanding of color to create specific effects in their paintings. Designers use their understanding of color to create visually appealing products and environments. And photographers use their understanding of color to capture beautiful and evocative images.
Overall, the connection between absorption and reflection and what makes blue is a fascinating and important topic with a wide range of applications in the real world.
The Sky and the Ocean
The sky and the ocean are two of the most iconic blue things in nature. But what makes them blue? The answer lies in the way that light interacts with the molecules in the air and water.
When sunlight hits the Earth's atmosphere, it is scattered in all directions by molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. However, blue light is scattered more than other colors of light because it has a shorter wavelength. This is because shorter wavelengths are more easily deflected by the molecules in the atmosphere.
The same thing happens in the ocean. When sunlight hits the water, it is scattered by molecules of water. However, blue light is scattered more than other colors of light because it has a shorter wavelength. This is why the ocean appears blue.
The scattering of blue light is also responsible for the blue color of many other things, such as the sky during twilight and the eyes of some animals.
The understanding of how light interacts with the molecules in the air and water is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps us to understand the nature of color and how we perceive it. Second, it has practical applications in a variety of fields, such as art, design, and photography.
For example, artists use their understanding of color to create specific effects in their paintings. Designers use their understanding of color to create visually appealing products and environments. And photographers use their understanding of color to capture beautiful and evocative images.
Overall, the understanding of how light interacts with the molecules in the air and water is a fascinating and important topic with a wide range of applications in the real world.
Blue in Nature
The connection between blue in nature and what makes blue is evident in the way that living organisms use light to their advantage. Blue light has a shorter wavelength than other colors of light, which means that it is more easily scattered and absorbed by molecules. This is why the sky and the ocean appear blue, and it is also why many flowers and animals have evolved to be blue.
For example, some flowers use blue pigments to attract pollinators. Bees and other insects are attracted to blue light, so flowers that are blue are more likely to be pollinated. Similarly, some animals use blue pigments to camouflage themselves from predators. Blue animals are less visible in water and in the sky, so they are less likely to be eaten.
The understanding of how blue light interacts with living organisms has a number of practical applications. For example, scientists are developing new ways to use blue light to treat diseases such as cancer and depression. Blue light has also been shown to improve sleep quality and reduce stress levels.
Overall, the connection between blue in nature and what makes blue is a fascinating and important topic with a wide range of applications in the real world.
Blue in Art and Culture
The connection between blue in art and culture and what makes blue is evident in the way that artists have used blue to evoke certain emotions and associations. Blue is often used to represent the sky and the ocean, which are both vast and awe-inspiring. It is also often used to represent peace and tranquility.
For example, the ancient Egyptians used blue to paint the sky and the Nile River in their tombs and temples. The Greeks and Romans also used blue to decorate their temples and palaces. In the Middle Ages, blue was often used in stained glass windows to represent the heavens.
In more recent times, blue has been used by artists to express a wide range of emotions and ideas. For example, Pablo Picasso used blue to express his sadness and despair during his Blue Period. Wassily Kandinsky used blue to represent spirituality and the cosmos. Yves Klein developed a signature shade of blue, which he called International Klein Blue, which he believed had metaphysical properties.
The understanding of the connection between blue in art and culture and what makes blue is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps us to understand the way that artists use color to create specific effects. Second, it helps us to appreciate the cultural significance of blue in different cultures around the world.
Blue in Science and Technology
The connection between blue in science and technology and what makes blue is evident in the way that scientists and engineers have harnessed the unique properties of blue light for a variety of applications.
- Lasers: Blue lasers are used in a variety of applications, including optical storage, laser surgery, and laser pointers. Blue lasers are more efficient than other types of lasers, and they can be focused more precisely. This makes them ideal for applications that require high precision, such as laser surgery.
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Blue LEDs are used in a variety of applications, including traffic lights, displays, and lighting. Blue LEDs are more energy-efficient than other types of LEDs, and they can produce a brighter light. This makes them ideal for applications that require high brightness and low energy consumption.
- Dyes and pigments: Blue dyes and pigments are used in a variety of applications, including clothing, paints, and cosmetics. Blue dyes and pigments are more stable than other types of dyes and pigments, and they can produce a wider range of colors. This makes them ideal for applications that require high color stability and a wide range of colors.
- Sensors: Blue sensors are used in a variety of applications, including medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring. Blue sensors are more sensitive than other types of sensors, and they can detect a wider range of substances. This makes them ideal for applications that require high sensitivity and a wide range of detection.
The understanding of the connection between blue in science and technology and what makes blue is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps us to understand the way that scientists and engineers are using the unique properties of blue light to develop new and innovative technologies. Second, it helps us to appreciate the potential of blue light for a variety of applications in the future.
FAQs about "What Makes Blue"
Here are some frequently asked questions about what makes blue:
Question 1: What is the science behind the color blue?
Answer: Blue is a color that is created when light with a wavelength between 450 and 495 nanometers is reflected off an object. When white light hits an object, some of the light is absorbed and some is reflected. The color of the object depends on which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected. Blue objects absorb red and green light and reflect blue light.
Question 2: Why does the sky appear blue?
Answer: The sky appears blue because of a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. This is the scattering of light by particles that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In the case of the sky, the particles that are scattering the light are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. Blue light has a shorter wavelength than other colors of light, so it is scattered more by the molecules in the atmosphere. This is why the sky appears blue.
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about what makes blue. For more information, please consult a reliable source.
Conclusion
Blue is a fascinating and complex color that has captured the human imagination for centuries. From the sky and the ocean to art and technology, blue is everywhere around us. In this article, we have explored some of the key aspects of what makes blue, including the science of light and wavelength, the absorption and reflection of light, the scattering of light in the atmosphere, and the cultural and scientific significance of blue.
The study of blue is a multidisciplinary field that draws on a variety of disciplines, including physics, chemistry, biology, art, and history. By understanding the science of blue, we can better appreciate the beauty and complexity of this remarkable color.
What Colors Make Blue and How Do You Mix Different Shades of Blue

What does blue and green make together?

What Colors Make Blue? Your Guide On How To Make Blue